Why Learning Hangul Matters
Hangul, the Korean alphabet, is often praised as one of the most scientific writing systems in the world. Its simple structure allows beginners to learn the basics in just a few hours. But beyond practicality, Hangul carries deep cultural meaning. Learning Hangul is like unlocking the key to Korea’s history, traditions, and modern identity.
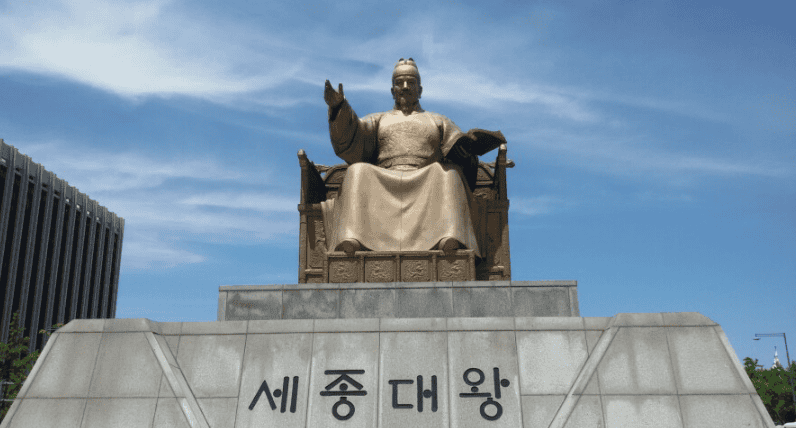


A Brief History of Hangul
King Sejong and the Creation of Hangul
In the 15th century, King Sejong the Great introduced Hangul to promote literacy among common people. Before this, Korea used classical Chinese characters, which were difficult for most citizens to master. Hangul gave everyone a chance to read and write.
Hangul’s Role in Literacy and Identity
Hangul dramatically improved literacy rates and became a foundation for Korean identity. It symbolized independence and equality, especially during times of foreign influence.
Modern Usage and Global Spread
Today, Hangul is not only used in Korea but also studied by learners worldwide, thanks to the global rise of K-Pop, Korean dramas, and interest in Korean culture.

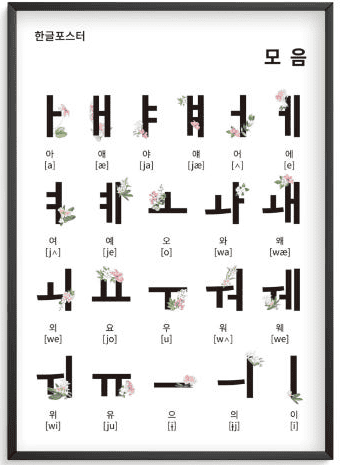
Structure and Features of Hangul
Consonants and Vowels
Hangul is made up of 14 basic consonants and 10 vowels. The letters are designed to represent the shape of the speaker’s mouth and tongue when pronouncing them. This scientific design makes Hangul unique among world writing systems.
Syllable Blocks
Unlike alphabets that write letters in a line, Hangul groups consonants and vowels into syllable blocks. For example, 한 (han) is composed of ㅎ + ㅏ + ㄴ. This block system gives Korean writing its distinctive square appearance.
Scientific and Logical Design
Linguists worldwide admire Hangul for its efficiency. King Sejong designed it so that even commoners could learn to read and write within days. Its logical structure reflects Korea’s emphasis on accessibility and equality.
[이미지 삽입 – 한글 음절 구조 예시]
- ALT (영문): Diagram showing how Hangul letters form syllable blocks.
- Description: Example of syllable construction in the Korean alphabet.
- 참고 링크: Pixabay – Hangul Blocks
Korean Language and Culture
Expressions of Respect (Honorifics)
The Korean language is rich with honorifics, reflecting deep respect for age and social status. Words change depending on who you’re speaking to, making politeness an essential part of communication.
Proverbs and Idioms
Korean sayings often reflect cultural values. For instance, “고생 끝에 낙이 온다” (After hardship comes happiness) reveals the importance of perseverance.
Influence of K-Pop, K-Dramas, and Media
Modern media has boosted global interest in learning Korean. Fans often pick up phrases from K-Dramas or lyrics from their favorite K-Pop songs, connecting entertainment with language learning.

Learning Korean Today
Language Schools and Online Platforms
Universities and institutes worldwide offer Korean language programs. Online platforms and apps also make learning Korean more accessible than ever.
Korean Language Proficiency Test (TOPIK)
For serious learners, the TOPIK exam measures Korean proficiency in reading, listening, and writing. It’s useful for students, workers, and anyone seeking opportunities in Korea.
Self-Study and Everyday Practice
From language exchange partners to YouTube lessons, many learners build skills by practicing daily. Watching Korean dramas with subtitles or keeping a simple diary in Korean are effective strategies.

How Hangul Connects People to Korean Identity
Hangul is more than an alphabet – it is a symbol of national pride and cultural resilience. Its creation by King Sejong represents equality, while its continued use unites modern Koreans with their heritage.
For global learners, Hangul offers more than practicality. It’s a way to connect with Korea’s music, films, food, and traditions – a gateway into the heart of Korean culture.
Leave a Reply